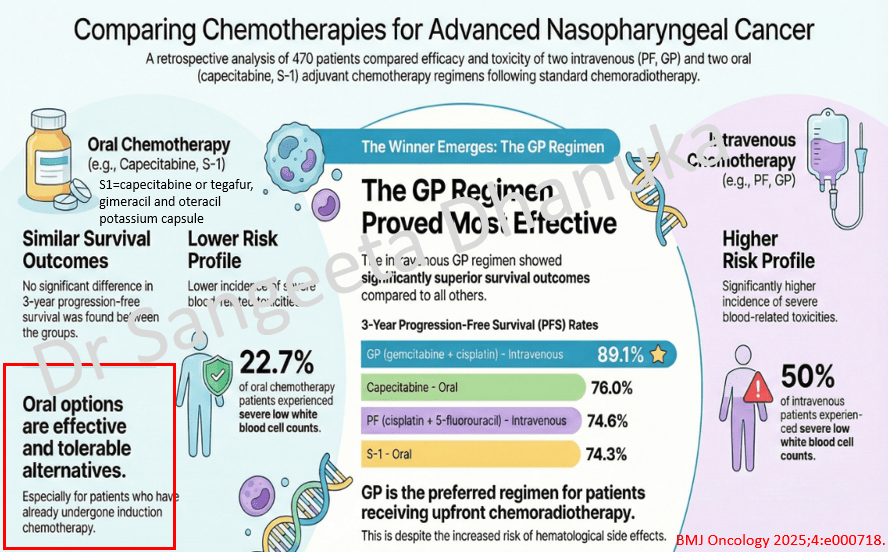
10 Jan 2026: Comparing Adjuvant Chemotherapies for Advanced Nasopharyngeal Cancer
This retrospective study evaluated the efficacy and safety of different adjuvant chemotherapy regimens for patients with locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma following concurrent chemoradiotherapy. The study found no significant difference in progression-free survival (PFS) between intravenous and oral administration. However, within the overall cohort, the GP regimen demonstrated a significantly superior 3-year PFS rate. For patients treated with induction chemotherapy and CCRT, oral chemotherapy, either with capecitabine or S1, was efficacious and tolerable.
The link to the full text is here https://bmjoncology.bmj.com/content/4/1/e000718
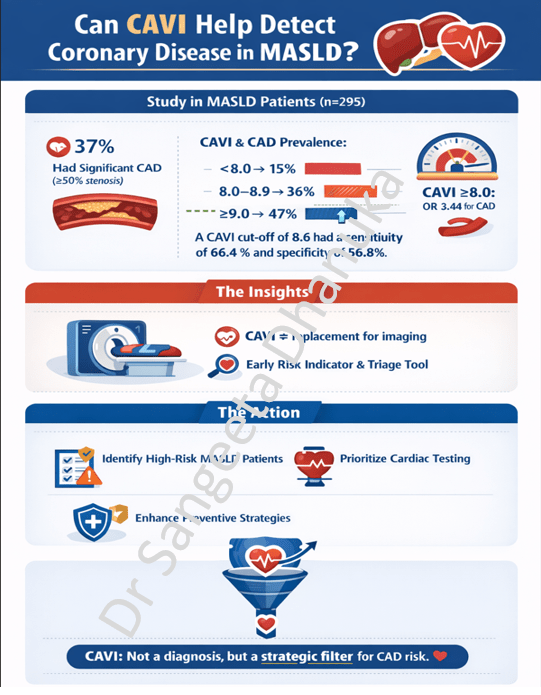
6 Jan 2026: Can CAVI Help Detect Coronary Disease in MASLD?
Patients with metabolic dysfunction–associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) have a high cardiovascular risk, yet there is no established, practical screening approach for detecting subclinical coronary artery disease (CAD) in this population. Coronary CT angiography (CCTA) is effective but resource-intensive. The study explores whether CAVI, a non-invasive measure of arterial stiffness, can help fill this gap.
Here is the link to the study. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2025.12.006
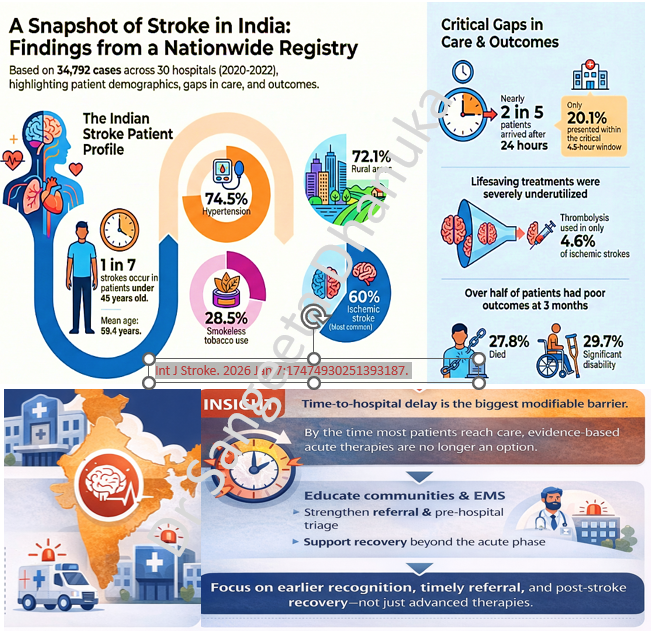
2 Jan 2026: A Snapshot of Stroke in India: Findings from a Nationwide Registry
This prospective study, based on the Hospital-Based Stroke Registries analyzed 34,792 stroke cases across 30 centers in India between 2020 and 2022 to identify patterns, risk factors, and long-term outcomes. The study highlights that stroke in India affects a relatively young population, and the rural incidence being very high. The data reveals a significant public health challenge characterized by late hospital arrival and underutilized acute treatments.
Here is the link to the study https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/17474930251393187
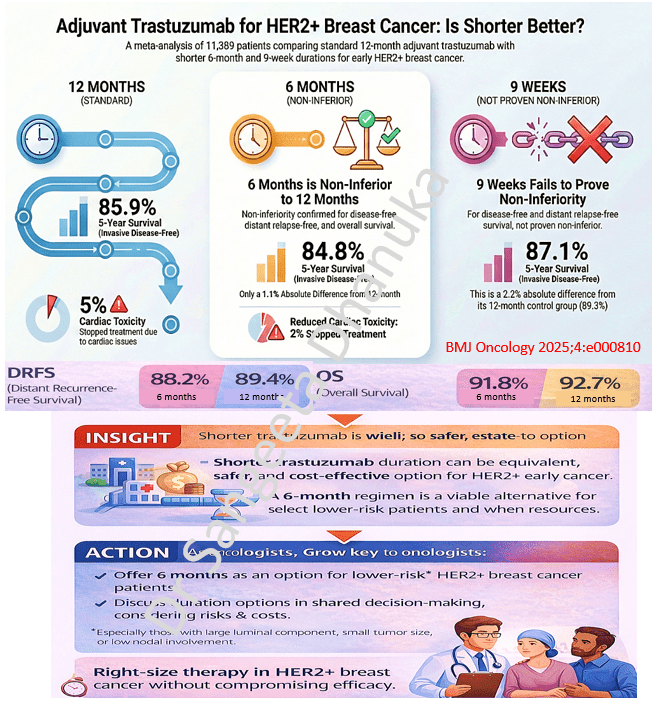
29 Dec 2025: Adjuvant Trastuzumab for HER2+ Breast Cancer: Is Shorter Better?
This systematic review and meta-analysis of 5 phase III non-inferiority trials, involving 11,389 patients, evaluated whether shorter durations of adjuvant trastuzumab are as effective as the standard 12-month regimen for HER2-positive early breast cancer. The study is unique as it is the first to utilize individual patient data (IPD) for this comparison, providing more reliable results than previous analyses. Based on this meta-analysis, 6 months of trastuzumab is a safe and effective option, specifically for patients at low risk of recurrence—those with small, node-negative, and ER-positive tumors. The study suggests that adopting a 6-month schedule can help patients avoid unnecessary physical, psychological, and financial toxicities while retaining nearly all the survival benefits of the longer course.
Here is the link to the full text https://bmjoncology.bmj.com/content/bmjonc/4/1/e000810.full.pdf
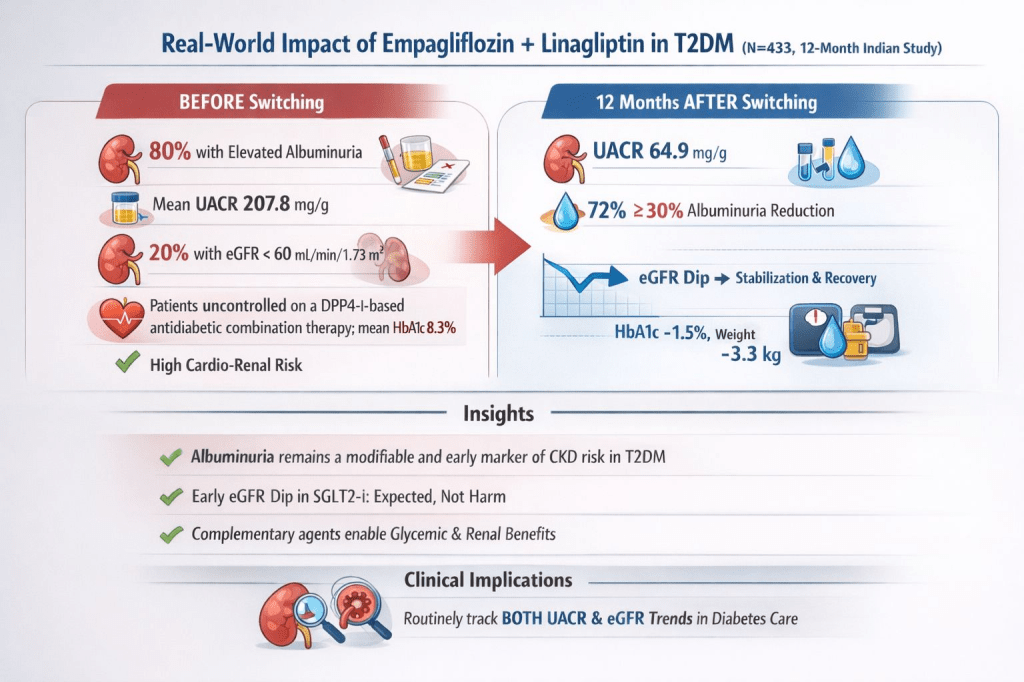
26 Dec 2025: Effectiveness of Empagliflozin-Linagliptin Fixed-Dose Combination on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes in a Real-World Setting
A recent 12-month Indian real-world study in adults with type 2 diabetes evaluated renal outcomes after initiating a fixed-dose combination of empagliflozin + linagliptin in SGLT2i–naïve patients previously uncontrolled on DPP-4 inhibitors. In this observational study, the use of FDC of empagliflozin and linagliptin for at least 12 months in T2DM patients previously uncontrolled on a DPP4-i-based regimen was associated with reductions in albuminuria and improvement in eGFR slope after the expected initial dip at three months. Improvements in glycemic control and body weight were also observed, regardless of underlying cardiometabolic risk.
The full text of the study is here: https://www.cureus.com/articles/423115-effectiveness-of-empagliflozin-linagliptin-fixed-dose-combination-on-chronic-kidney-disease-outcomes-in-patients-with-type-2-diabetes-in-a-real-world-setting#!/
22 Dec 2025: Should we evaluate pathological complete response (pCR) with chemo in stage I triple-negative breast cancer patients?
New study shows prognostic importance of pathological complete response (pCR) to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC)
Importance of the study: Since most clinical trials for TNBC focus on stage II/III, little is known on the impact of NACT in stage I disease
🟣 Patients were treated with anthracycline-taxane-based neoadjuvant chemo, and 57.3% had a pCR
🟣 Platinum-based treatment did not significantly improve the pCR rate
🟣 Patients with residual disease, who received adjuvant capecitabine, did not show significant improvement in OS
🟣 pCR was associated with a favorable long-term outcome
The infographic below shows how this new data might influence conversations between oncologists, and the key implications for clinical practice
The full text of the study is here https://www.esmoopen.com/article/S2059-7029(25)01793-4/fulltext
15 Dec 2025: Bone health in patients with diabetes: ADA 2026
Age-specific fracture risk is significantly increased in people with type 1 or type 2 diabetes in both sexes, with a 34% increase in fracture risk compared with those without diabetes
Longer diabetes duration further increases fracture risk
Hence, HCPs should assess fracture history and risk factors in people with diabetes and recommend measurement of BMD if appropriate, according to the individual’s age and sex.
The document provides a detailed discussion, with relevant references on bone health in diabetes and why and how long-term diabetes increases the risk of fracture. The link to the publication is here https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/49/Supplement_1/S61/163931/4-Comprehensive-Medical-Evaluation-and-Assessment
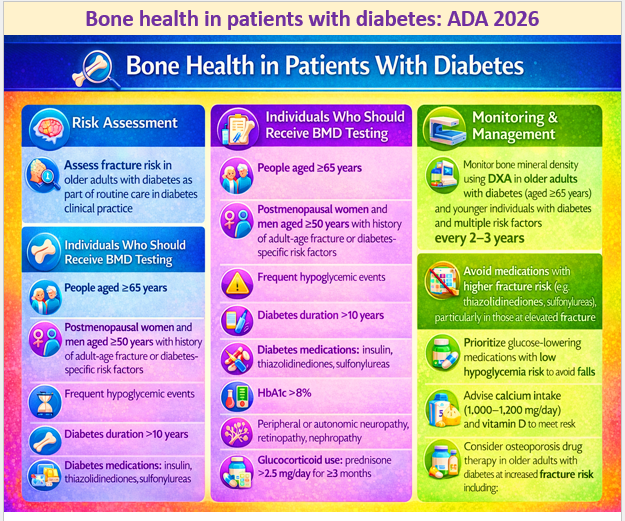
12 Dec 2025: Diagnosis and screening for type 2 diabetes in adults: ADA 2026
The full text on Diagnosis and screening is here https://diabetesjournals.org/care/article/49/Supplement_1/S27/163926/2-Diagnosis-and-Classification-of-Diabetes
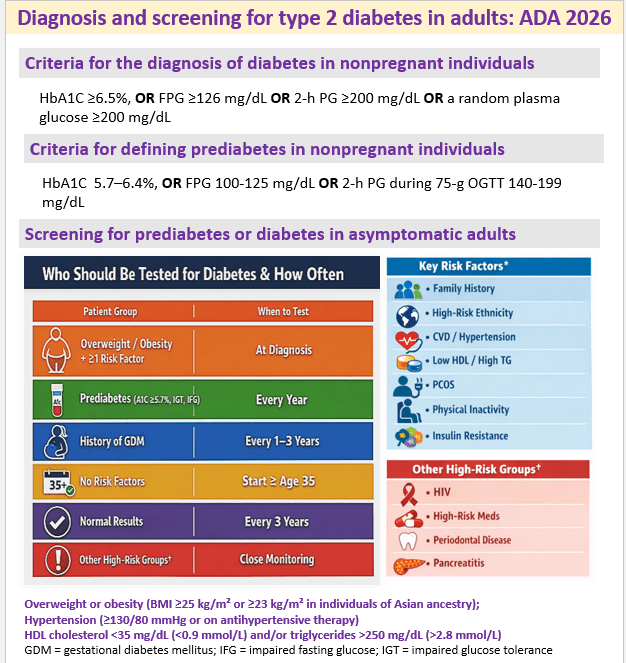
9 Dec 2025: RAS inhibitors+ dapagliflozin + finerenone in diabetic kidney disease with nephrotic-range proteinuria: RWE
This is the first real-world study that evaluated the effects of triple therapy with RAS inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, and finerenone in DKD patients having nephrotic-range proteinuria
The results showed that this triple therapy may be an effective option to reduce proteinuria and albuminuria in such patients, while also slowing chronic kidney disease progression.
The current drawback of the study is the small sample size. But I am sure these outcomes will spur further studies of this triple combination
Here is the link to the study https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-27239-8
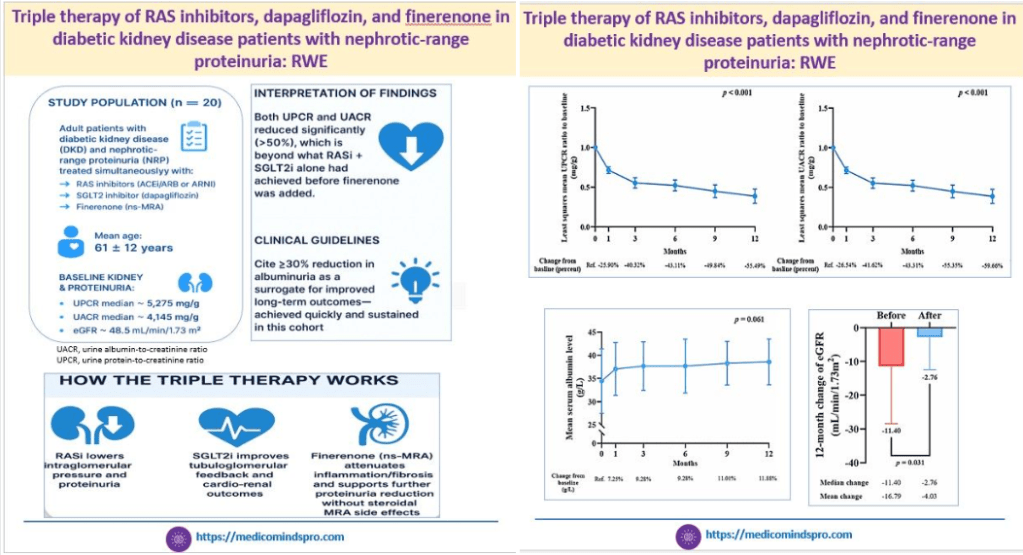
6 Dec 2025: Are we moving to Single antiplatelet therapy (SAPT) even after CABG?
Patients who undergo Coronary-artery bypass grafting (CABG) for an acute coronary syndrome are considered a high-risk group, for whom standard Dual Antiplatelet Therapy (DAPT) is recommended
But the recently published data of the TACSI study show that DAPT for 1 year was not superior to aspirin alone after CABG.
Here is the link to the study https://www.nejm.org/do/10.1056/NEJMdo008283/full/
3 Dec 2025: Dapagliflozin induces early cardiorenal protection in individuals at different levels of cardiovascular risk irrespective of the presence or absence of diabetes
This new study slated published in the 2026 issue of Hypertension journal, investigated the cardiorenal effects of dapagliflozin in patients at cardiovascular risk, with or without type 2 diabetes.
It shows that dapagliflozin improves early cardiovascular and kidney health markers after 12 weeks in patients at varying cardiovascular risk, with or without type 2 diabetes. The results show that early use of SGLT2 inhibitors may help prevent cardiovascular and kidney disease in at-risk individuals.
The paper also explains how SGLT2 inhibition leads to cardiovascular and kidney protection. The sample size is small, but it raises the possibility that SGLT2 inhibitors could be effective in the primary prevention of cardiovascular and kidney complications
Here is the link to the full text https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.125.25955?casa_token=Hi2vgrJLxfsAAAAA%3AzNicAQ3JwIoQlcZT2tHaXEgLuDFpWpR6Jq-IsguTx-0FKch8j_pk0MGxNk7N2e6NaMwsWk5PLMLZbQ
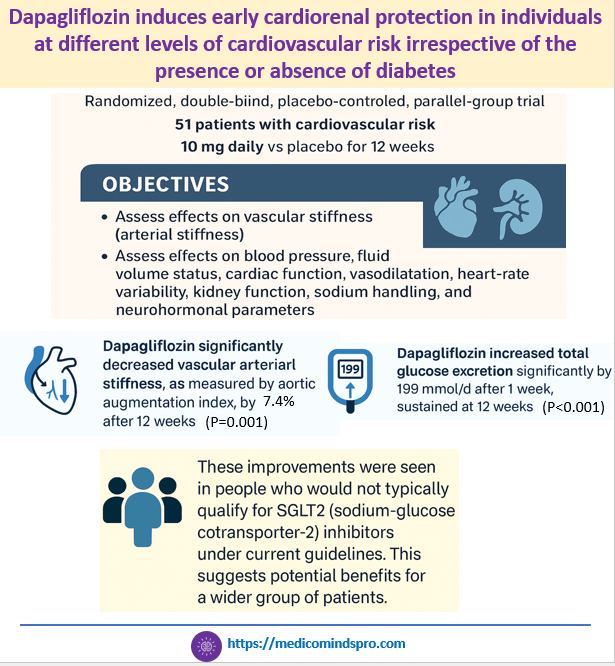
30 Nov 2025: MRI-confirmed improvement in MASLD with empagliflozin
While the beneficial effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on MASLD in patients with diabetes is known, most studies have used only fibrosis indices or liver ultrasound for evaluation
This study used MRI for evaluation. Most patients had grade 2 or 3 steatosis on MRI at baseline. There was a confirmed greater improvement in the empagliflozin group, with 94% showing grade 1 or lower steatosis on ultrasound and 100% achieving grade 0 on MRI (p < 0.001 for both).
Here is the link to the study https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12664258/
The graphic below is a depiction of how the study might shape conversations between HCPs and patients
22 Nov 2025: New hope for patients with oral steroid-dependent, severe, uncontrolled asthma
The WAYFINDER study evaluated the ability of tezepelumab to enable patients with oral steroid-dependent, severe, uncontrolled asthma to reduce or discontinue oral steroid (OCS) use without loss of asthma control.
After 52 weeks, nearly 90% of patients had a maintenance OCS dose of 5 mg/day or less, and more than 50% completely discontinued OCS. The graphics below convey the patient benefits through emotions involving not just the patient but the caregiver and clinician, too.
Read the full text here: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanres/article/PIIS2213-2600(25)00359-5/fulltext

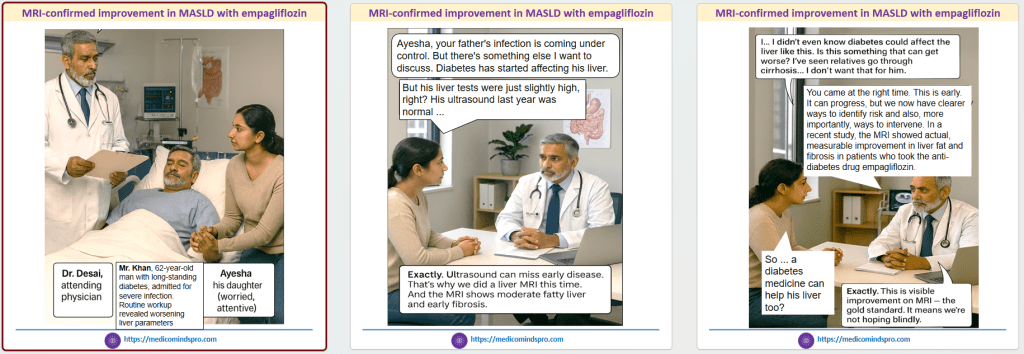
19 Nov 2025: Triple Versus Dual Lipid-Lowering Therapy in Acute Coronary Syndrome
This study compared the efficacy and safety of triple LLT (high-dose, high-intensity statin+ezetimibe+bempedoic acid) vs standard of care (high-dose, high-intensity statin+ezetimibe) after ACS
Adding bempedoic acid to statin–ezetimibe therapy in the setting of ACS was safe but failed to improve the percentage of patients achieving the LDL-C goal (<55 mg/dL) at 8 weeks.
Here is the link to the publication https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.125.075388
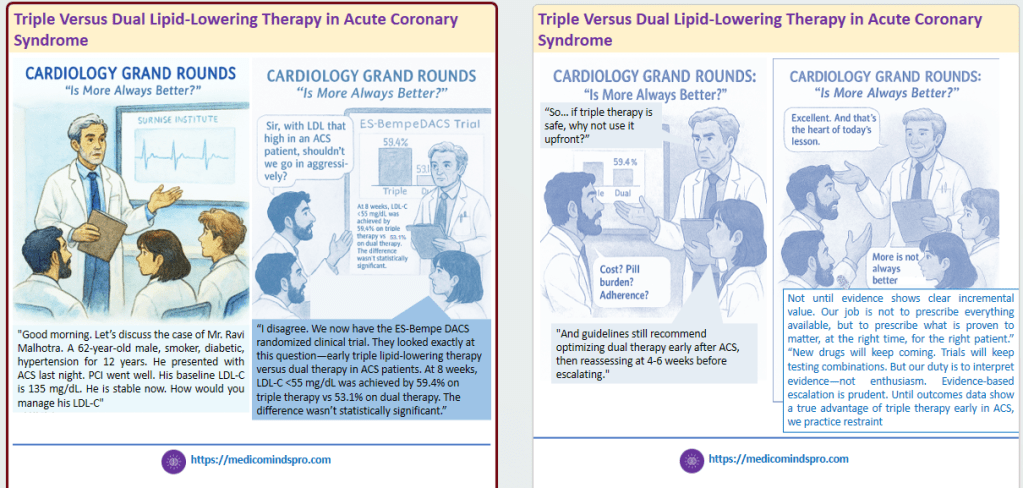
16 Nov 2025: Impact of amlodipine on BP variability on cardiovascular and renal outcomes in patients with diabetes
This study evaluated the relationship between visit-to-visit BPV and cardiovascular events, renal outcomes, and mortality in individuals with and without diabetes, using data from the ASCOT trial
Authors suggest that long-acting calcium channel blockers should be included into treatment strategies to improve cardiovascular outcomes.
The infographics below show how this data can be shared creatively in CME slide decks or through in-clinic communication
Here is the link to the publication https://journals.lww.com/jhypertension/abstract/2025/12000/the_impact_of_blood_pressure_variability_on.15.aspx
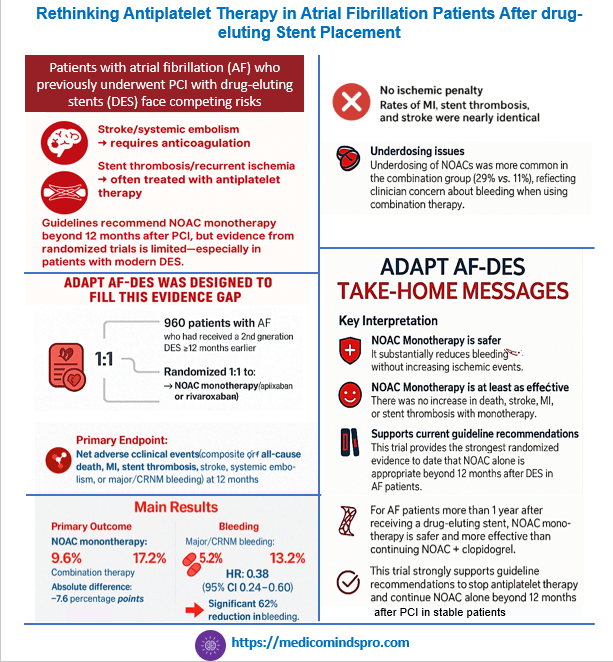
13 Nov 2025: Rethinking Antiplatelet Therapy in Atrial Fibrillation Patients After drug-eluting Stent Placement
A recently published study has shown that among patients with atrial fibrillation who had undergone implantation of a drug-eluting stent at least 1 year earlier, NOAC monotherapy was noninferior to combination therapy for net adverse clinical events.
This data strongly reinforces the ESC and ACC/AHA guidelines to stop antiplatelet therapy and continue NOAC alone beyond 12 months after PCI in stable patients.
This is now the most robust randomized evidence supporting NOAC monotherapy in AF patients with prior PCI. The study can be accessed at https://www.nejm.org/doi/pdf/10.1056/NEJMoa2512091
10 Nov 2025: Prasugel-based DAPT better than ticagrelor-based DAPT in Indian patients with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes who had undergone drug-eluting stent placement
This data from the TUXEDO-2 trial was presented at AHA 2025. It was conducted at 66 centers in India, and included 1,800 adults. This was an interesting result, as currently, these medications are treated as interchangeable. Read more here https://newsroom.heart.org/news/effectiveness-of-anti-clotting-meds-after-stent-placement-varied-in-people-with-diabetes

5 Nov 2025: How long should CGM be worn by patients with diabetes for a meaningful difference in glycemic control?
This study in 9258 adults published last week found that wearing CGM for >75% or more of days over the 12-month period was associated with improved glycemic control compared with infrequent or no use of CGM. The study also found that 6 months post-CGM initiation may be a critical time to focus counseling on continuing CGM use, as compliance begins to dip at this time point due to therapeutic inertia. Here is the link to the study https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2840792


30 Oct 2025: Budesonide–formoterol versus salbutamol as reliever therapy in children with mild asthma (CARE)
The CARE study has shown that Combination inhaled corticosteroid–formoterol reliever monotherapy reduces the rate of asthma attacks compared to short-acting β2-agonist (SABA) reliever monotherapy in children by 45%. The study suggests a New Approach to Acute Pediatric Asthma
Link to the study https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(25)00861-X/abstract
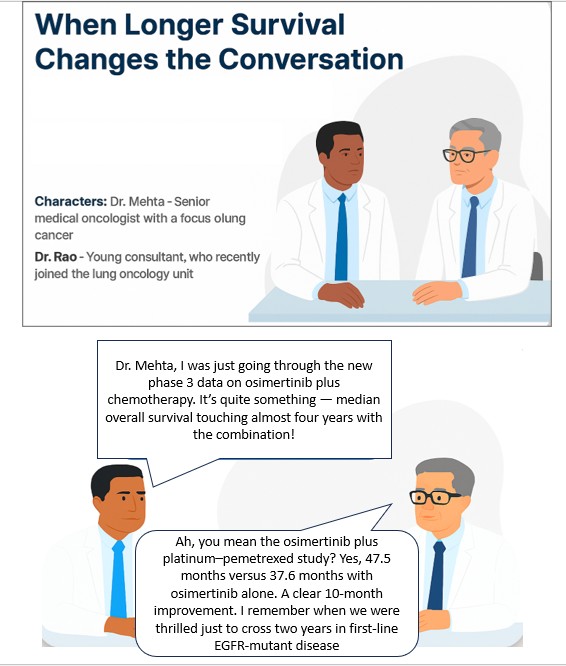
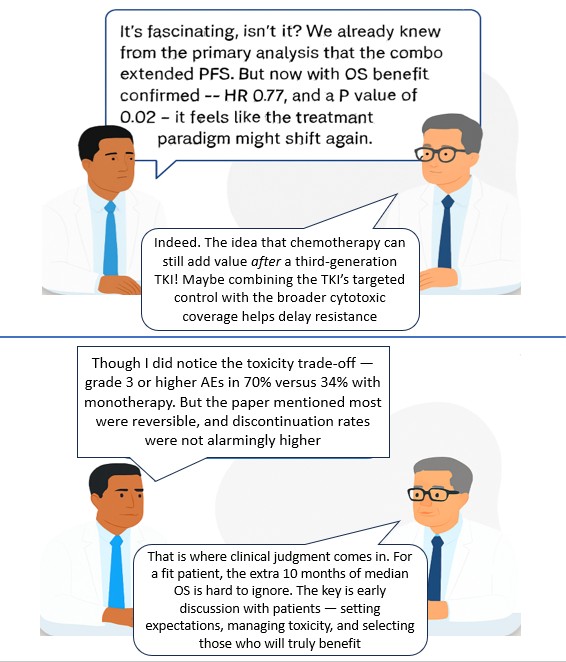
25 Oct 2025: Survival with Osimertinib plus Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC
The recently released results of the FLAURA 2 trial are likely to generate considerable interest among oncologists treating lung cancer (NSCLC).
The study showed that in patients with EGFR-mutated (exon 19 deletion or L858R mutation) advanced NSCLC, first-line treatment with osimertinib plus platinum–pemetrexed led to significantly longer overall survival than osimertinib monotherapy. However, it was associated with an increased risk of reversible adverse events of grade 3 or higher.
Right patient selection at the right time will remain the key here. A patient who has perhaps a good ECOG PS and can tolerate the adverse effects better might be the best candidate for this treatment. That will clinically mean it is important to perform NGS testing as soon as possible.
Publication link https://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMoa2510308
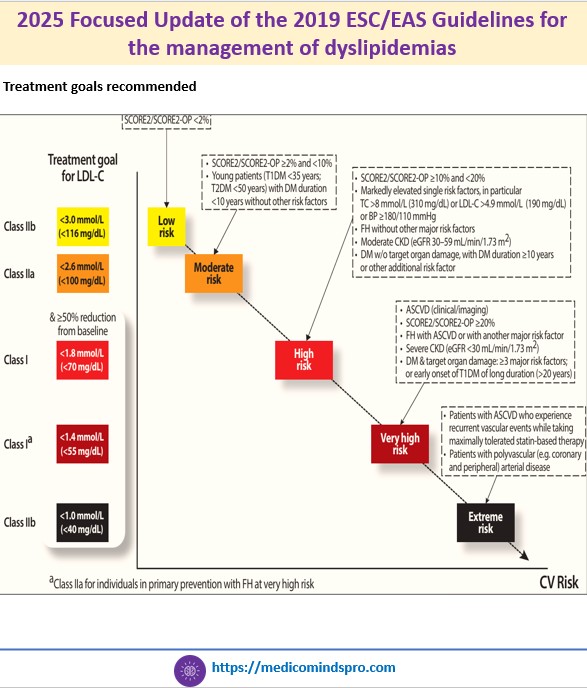
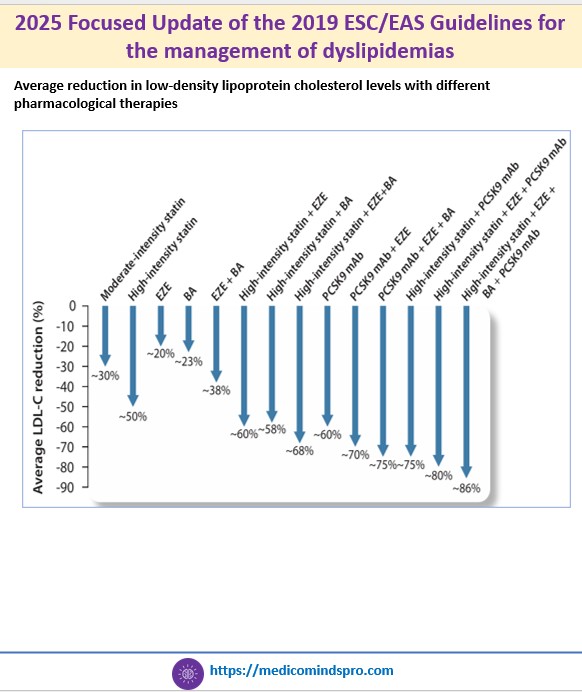
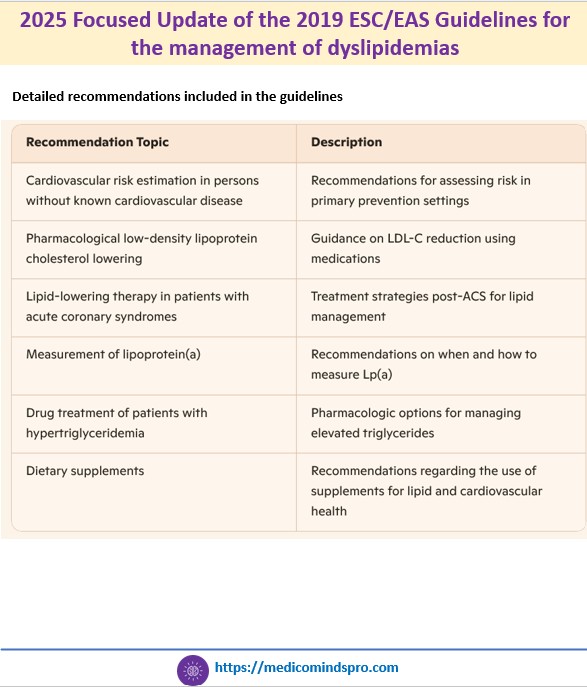
19 Oct 2025: 2025 Focused Update of the 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias
An updated guideline has been published by the ESC and EAS regarding the management of dyslipidemias. All new recommendations included in this Focused Update are an addition to the recommendations of the 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines and do not replace the 2019 guidelines.
Some highlights include
🟣 The guideline now recommends using SCORE2 and SCORE2-OP, rather than the original SCORE algorithm for risk estimation. These updated tools use non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol instead of total cholesterol and are calibrated to national CVD mortality rates
🟣 Recommendations on non-statin agents like ezetimibe, PCSK9 inhibitors, or bempedoic acid
🟣 Early and intensive LDL-C lowering during hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome
🟣 The update reinforces that dietary supplements and vitamins lack sufficient evidence
Publication link: https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/46/42/4359/8234482?login=false#529497870
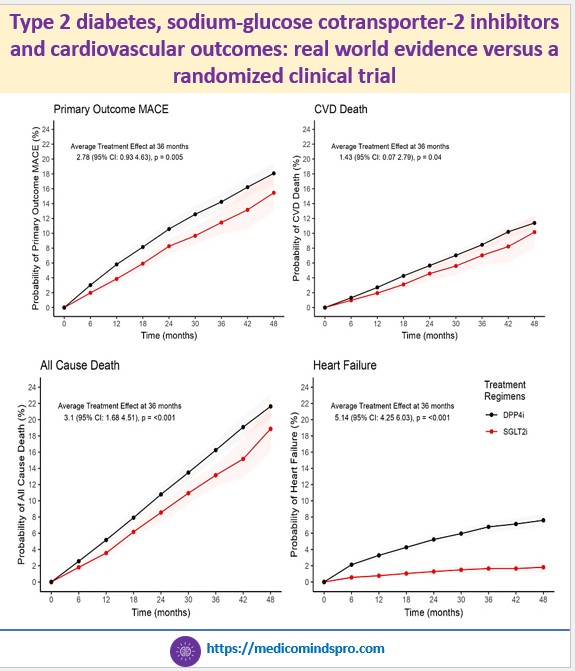
15 Oct 2025: Type 2 diabetes, sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes: real world evidence versus a randomized clinical trial
A new Danish study published in Cardiovascular Diabetology offered clarity. Using real-world data from over 13,000 patients with T2D and established cardiovascular disease, researchers emulated the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial—but with a twist: Patients were older, frailer, and less adherent than those in trials. Yet the findings were striking. The benefits were more pronounced in patients over 65 years, showing the therapy’s value where the need is greatest. By mimicking real-world adherence and treatment dynamics, the study reaffirms that SGLT2is provide consistent, clinically meaningful benefits beyond clinical trials.
Publication link: https://cardiab.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12933-025-02924-0
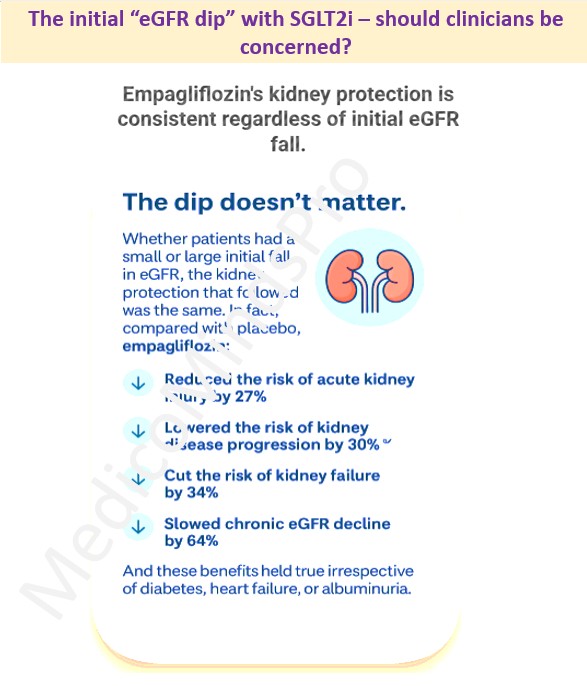
9 Oct 2025: Effects of empagliflozin on conventional and exploratory acute and chronic kidney outcomes
The “eGFR dip” is a psychological barrier for many clinicians — a signal that seems to say ‘wait’. But the latest data from a meta-analysis of over 23,000 participants across four landmark trials — EMPA-REG OUTCOME, EMPEROR-Reduced, EMPEROR-Preserved, and EMPA-KIDNEY — told a different story. Using individual participant-level data, the researchers asked a crucial clinical question: “Does this dip predict harm, or is it simply part of how the drug works?”
The answer: the dip doesn’t matter. Whether patients had a small or large initial fall in eGFR, the kidney protection that followed was the same. The authors suggest that routine early re-testing may be unnecessary because the dip is transient and benign. The conclusion: a transient fall does not equal renal injury — it may signal renal protection taking effect. Read the paper here https://www.thelancet.com/journals/landia/article/PIIS2213-8587(25)00222-0/fulltext
6 Oct 2025: Key changes in the new AHA 2025 hypertension guidelines
The AHA guidelines for hypertension were recently updated. While there is a long list of what is new, there are some updates that most clinicians, including general practitioners, must know. The link to the guidelines is https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIR.0000000000001356

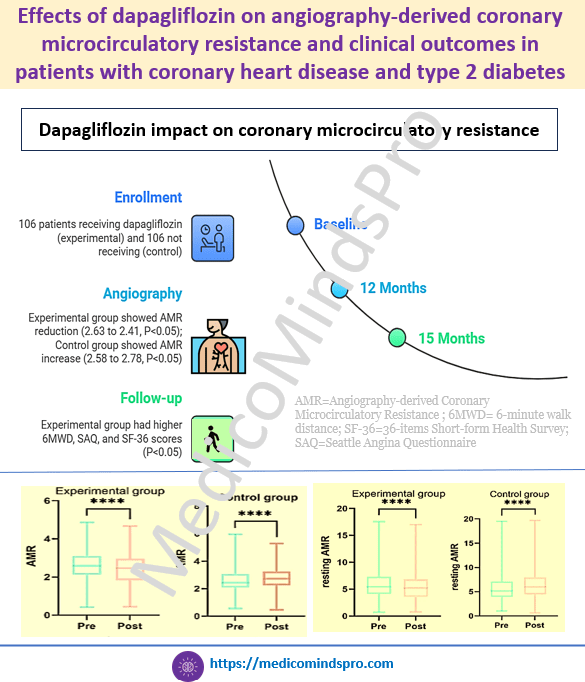
3 Oct 2025: Effects of dapagliflozin on angiography-derived coronary microcirculatory resistance and clinical outcomes in patients with coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes
Coronary microvascular dysfunction is prevalent in patients with coronary heart disease and Type 2 Diabetes. SGLT2is have cardioprotective effects; however, their impact on microcirculatory function is not known. This study evaluated the effects of dapagliflozin on microcirculatory function and clinical outcomes in patients with CHD and T2DM. Beneficial effects of dapagliflozin were seen on coronary microcirculatory function, exercise capacity, quality of life, and survival in patients with CHD and T2DM.
Here is the study link https://dmsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13098-025-01916-0
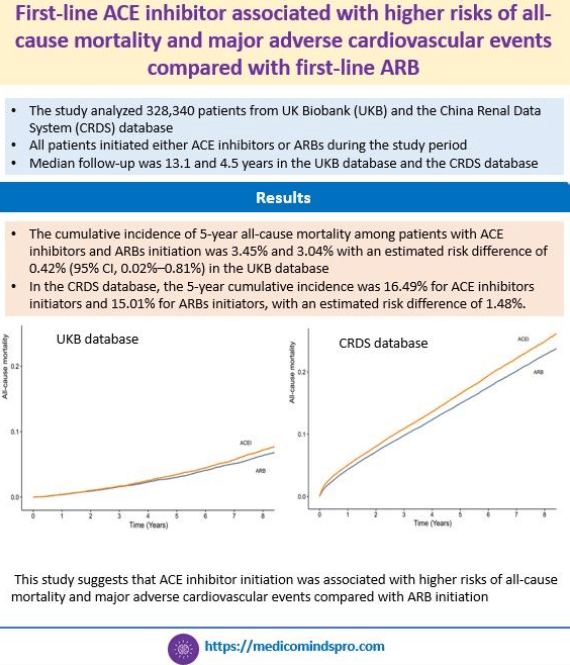
30 Sept 2025: First-line ACE inhibitor associated with higher risks of all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events compared with first-line ARB
This study shows that shows that ACE inhibitor initiation for hypertension was associated with higher risks of all-cause mortality and major adverse cardiovascular events compared with ARB initiation. This was a comprehensive evaluation based on real-world data from 2 large longitudinal cohorts comparing all-cause mortality between ARBs and ACE inhibitors during a long-term follow-up. This data is important because guidelines for managing hypertension and chronic kidney disease generally do not discriminate between ACE inhibitors and ARBs in recommending one over the other
Here is the full text link: https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.125.25549
26 Sept 2025: Practical Recommendations on Sunscreen Use for Indians
The way this consensus is written is likely to be useful for common people as well because it also provides details on what the labels on sunscreen packs mean and what to check besides the SPF. The statements are a mix of tables and graphics- I would say a more interesting way to present them. This is the era of media and graphics, and using them creatively in publications certainly enhances the presentation. Check the full text here https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12439021/#jocd70441-sec-0042

23 Sept 2025: Assessment of metabolic dysfunction‐associated fatty liver disease in primary care
This evidence‐based consensus statement summary provides recommendations for the assessment and monitoring of adults with MAFLD in primary care. The statements have been listed in a Table in a Q&A format, which is a useful quick glance for clinicians. Here is the full text https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/1750743X.2025.2548754#abstract
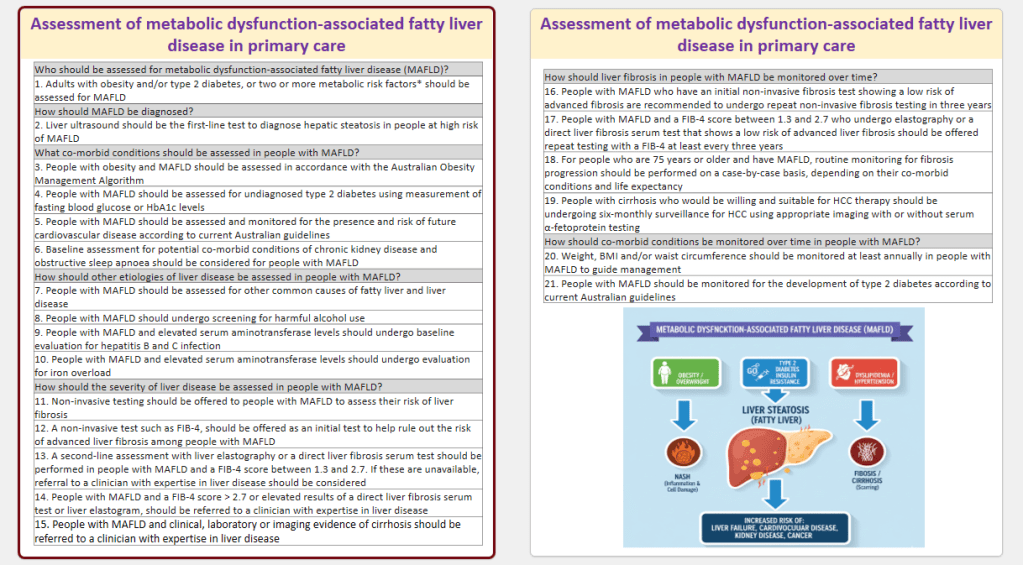
20 Sept 2025: Low-Dose Aspirin for PI3K-Altered Localized Colorectal Cancer
In this study, aspirin led to a significantly lower incidence of colorectal cancer recurrence than placebo among patients with PIK3CA hotspot mutations in exon 9 or 20 and appeared to have a similar benefit among those with other somatic alterations in PI3K pathway genes. Link to the full text https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2504650
17 Sept 2025: In patients with HFrEF and COPD, beta-blocker (metoprolol, bisoprolol, carvedilol, or nebivolol) use is associated with lower risk of cardiovascular death/total heart failure hospitalizations
This real-world study, with a large sample size of 5084 patients with HFrEF and COPD, proves that in patients with comorbid HFrEF and COPD, the significant cardiovascular benefits of beta-blockers outweigh potential concerns for respiratory safety regardless of COPD GOLD group.
Here is the link to the full text https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1002/ejhf.70046

14 Sept 2025: 2025 ESC/EACTS Guidelines for the management of valvular heart disease
This update has made some important changes in recommendations for TAVI. Most importantly, the age cutoff for TAVI vs SAVR has been lowered from 75 to 70 years, making it more closer to the American recommendations. Link https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf194/8234488?login=false

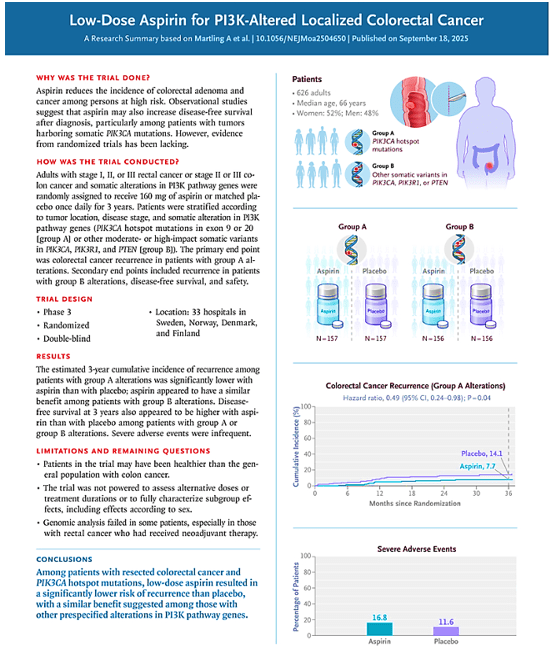
11 Sept 2025: Beta-Blockers after Myocardial Infarction in Patients without Heart Failure
The study showed that among patients with a myocardial infarction and a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 40%, beta-blocker therapy led to a lower risk of death or major adverse cardiovascular events than no beta-blocker therapy. Link https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2505985
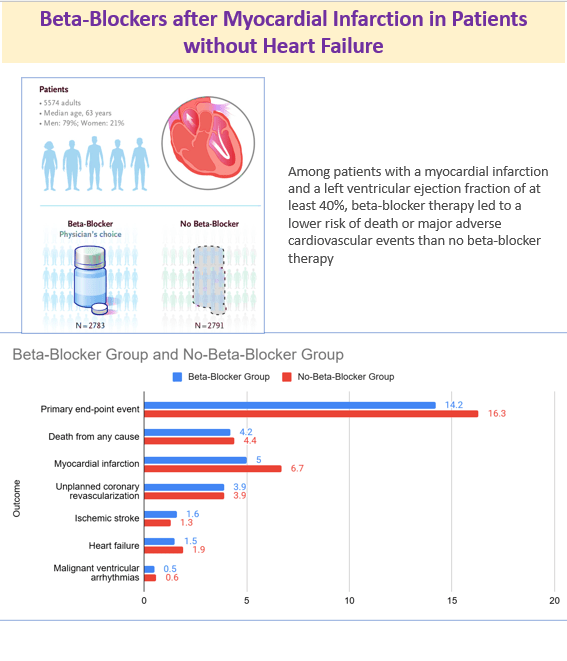
8 Sept 2025: Adding empagliflozin to ongoing metformin improves metabolic profile, TG-G and fib-4 index and liver function tests in type 2 diabetic patients with MAFLD
Adding empagliflozin to ongoing metformin improves metabolic profile, TG-G and fib-4 index: Adding empagliflozin to ongoing metformin significantly improved metabolic and liver-related markers in T2DM patients with MAFLD. Link https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17446651.2025.2550733?src=
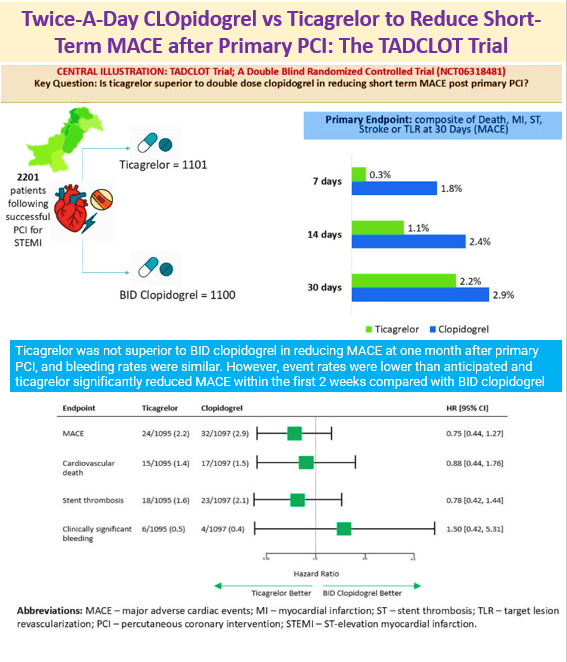
5 Sept 2025: Twice-A-Day CLOpidogrel vs Ticagrelor to Reduce Short-Term MACE after Primary PCI: The TADCLOT Trial
Ticagrelor was not superior to BID clopidogrel in reducing MACE at one month after primary PCI, and bleeding rates were similar. However, event rates were lower than anticipated and ticagrelor significantly reduced MACE within the first 2 weeks compared with BID clopidogrel. Link to the article https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacc.2025.08.041
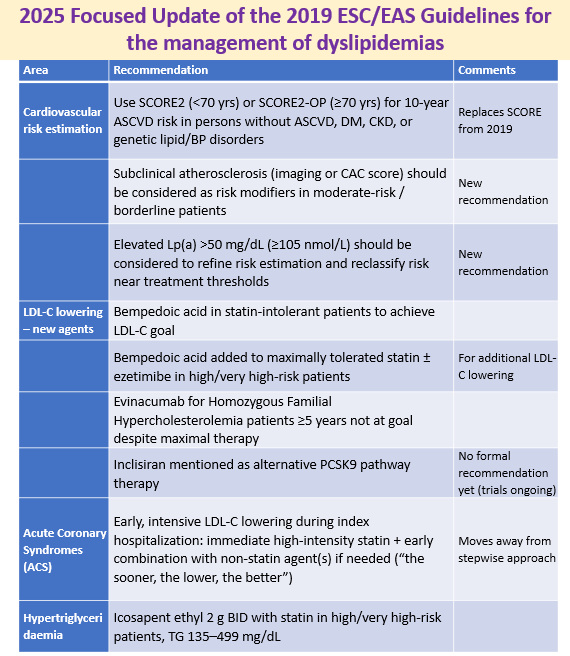
2 Sept 2025: 2025 Focused Update of the 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemias
An important update is the new risk calculation scores and other parameters of risk estimation. Another important one is early. intensive intervention in ACS rather than step-wise approach. Full text link https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf190/8234482?login=false
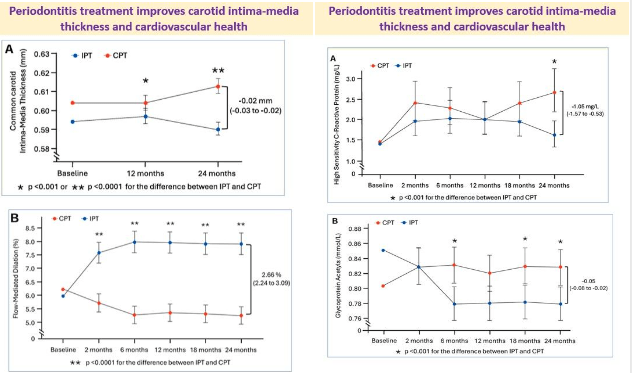
31 Aug 2025: Periodontitis treatment improves carotid intima-media thickness and cardiovascular health
Did you know that treatment of gum disease can improve cardiovascular health?
This is exactly what a new study has shown
Patients: 135 patients with periodontitis
Treatment: Intensive periodontal treatment (IPT) including scaling, root planning, and, when appropriate, surgical corrective therapy or control periodontal treatment (CPT) including supra-gingival scaling and polishing
Carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT), vascular phenotype, and inflammatory markers evaluated over 2 years
Treatment of periodontitis improved endothelial function, reduced systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, and favorably modified structural vascular health
The article also explains why and how the improvement occurs. Here is the full text https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/advance-article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehaf555/8237946?login=false
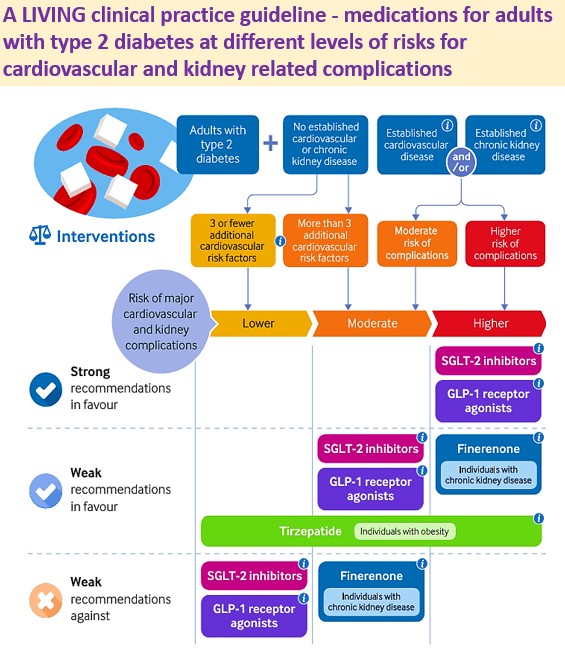
27 Aug 2025: A LIVING clinical practice guideline – medications for adults with type 2 diabetes at different levels of risks for cardiovascular and kidney related complications
Why this separate guideline?
1️⃣ Most guidelines provide recommendations for adults with established cardiovascular or kidney disease
2️⃣ However, they do not provide recommendations based on the level of risk within each disease category in a patient
3️⃣ Current guidelines do not provide risk-stratified effects for outcomes of benefit and harm
4️⃣ To help clinicians provide customized care using a risk-stratification approach
For which patients is this guideline applicable?
☑️ All adults with type 2 diabetes, irrespective of ethnicity, sex, or comorbidities
☑️ Adults with or without concomitant cardiovascular risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and/or chronic kidney disease
Medications covered in this guideline
✅ SGLT-2 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, finerenone, and tirzepatide
Added features
📲 MAGICapp – interactive, providing recommendations, evidence summaries with risk-stratified benefits and harms for each medication, and more detailed explanations regarding guideline methods
Future plan
⏭️ De-prescription, Combinations, Refined baseline risk estimates, Refined risk stratification approach.
Link to the full text https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12355350/#sec8
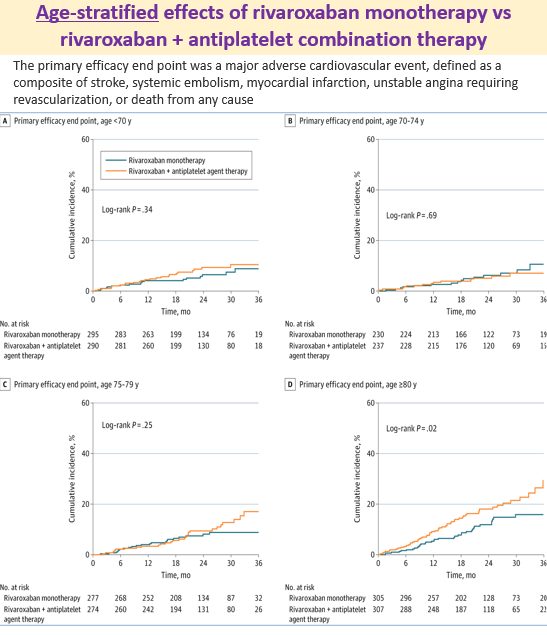
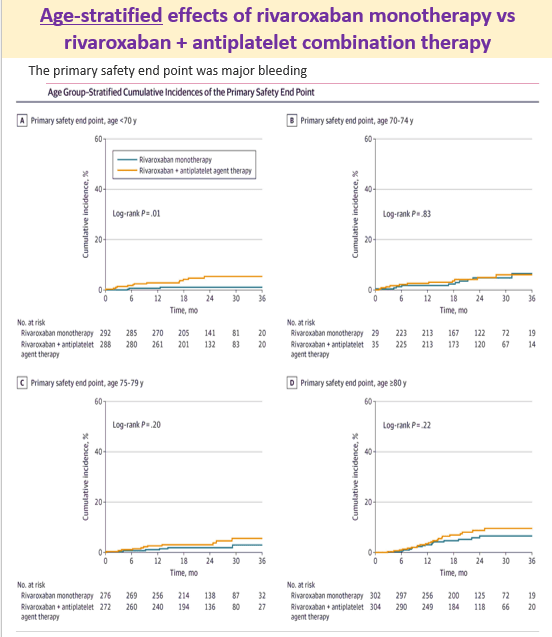
24 Aug 2025: Does the effect of rivaroxaban monotherapy differ from rivaroxaban-antiplatelet therapy depending on age?
Patients: 2215 patients with CHADS2 score 1 or more, Stable Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) and atrial fibrillation
Primary efficacy endpoint: major adverse cardiovascular event, defined as a composite of stroke, systemic embolism, myocardial infarction, unstable angina requiring revascularization, or death from any cause.
Safety endpoint: major bleeding
What was found? : Rivaroxaban monotherapy reduced the risk of major cardiovascular events and major bleeding across all age groups, especially in older patients with AF and stable CAD.
Link to the study https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamacardiology/article-abstract/2837457
21 Aug 2025: Comparative efficacy of antihypertensives in reducing the risk of new-onset or recurrent atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients with hypertension, diabetes, and/or AF
In this network meta-analysis, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors plus thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors, and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) were the most effective in reducing AF events, outperforming placebo and calcium channel blockers (CCBs). Link to the publication https://academic.oup.com/eurjpc/advance-article-abstract/doi/10.1093/eurjpc/zwaf335/8180368?redirectedFrom=fulltext&login=false

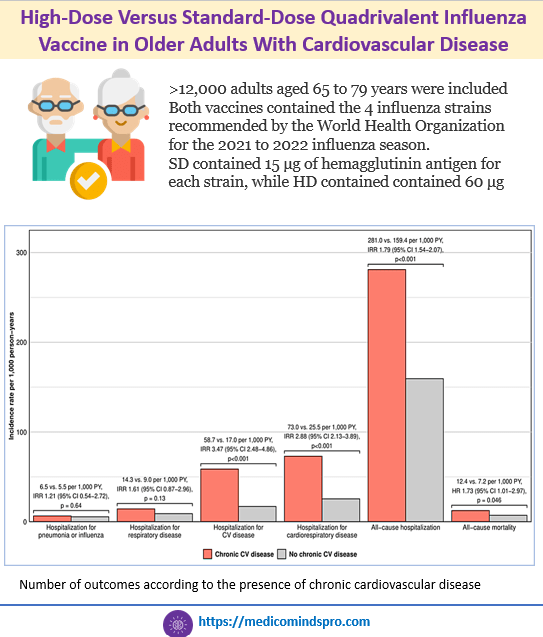
18 Aug 2026: High-Dose Versus Standard-Dose Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease
High-Dose Versus Standard-Dose Quadrivalent Influenza Vaccine in Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease. It is known that High-dose (HD) influenza vaccine compared with standard dose (SD) is associated with a lower risk of adverse outcomes in older adults, including cardiorespiratory hospitalizations and mortality. This study showed that HD compared with SD influenza vaccine was associated with a reduced incidence of hospitalizations for pneumonia or influenza and a reduced incidence of all-cause mortality regardless of chronic CVD, HF, IHD, and atrial fibrillation. Publication link https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.124.011496
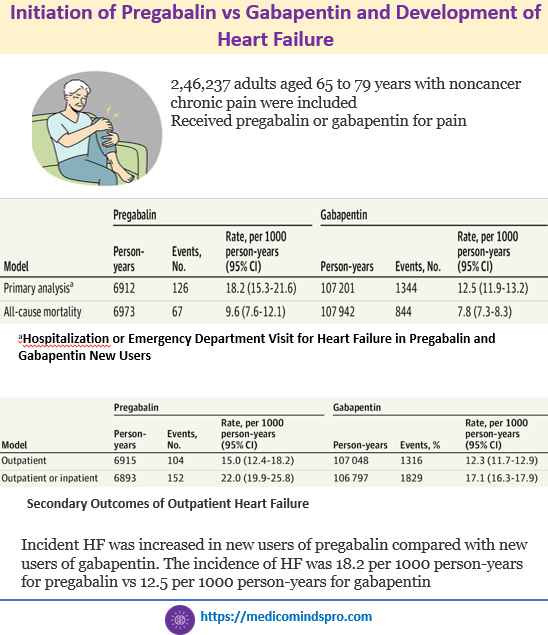
15 Aug 2026: Initiation of Pregabalin vs Gabapentin and Development of Heart Failure
Is pregabalin associated with a higher incidence of heart failure (HF) compared with gabapentin? In this cohort study of 246,237 patients aged 65 to 89 years with noncancer chronic pain, pregabalin was associated with a higher incidence of HF compared with gabapentin. The findings suggest that pregabalin should be prescribed with caution in older patients with noncancer chronic pain. Publication link https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2837132
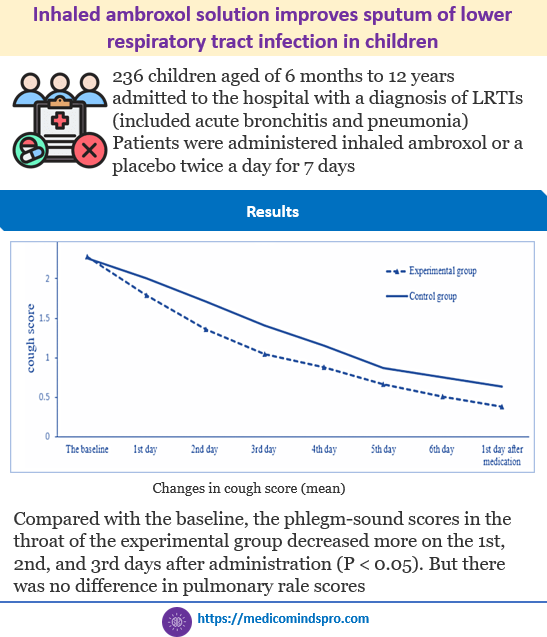
12 Aug 2025: Inhaled ambroxol solution improves the sputum of lower respiratory tract infection in children
Inhaled ambroxol solution improves the sputum of lower respiratory tract infection in children. Until now, there was not much data on the efficacy of inhaled ambroxol in children. Moreover, this is data in hospitalized children and could be very useful.
Link to the full text https://bmcpulmmed.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12890-025-03845-0
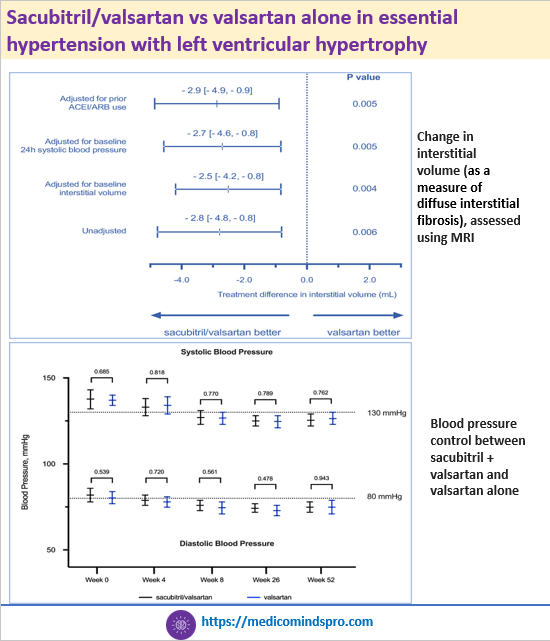
9 Aug 2025: Sacubitril/valsartan vs valsartan alone in essential hypertension with left ventricular hypertrophy
Hypertensive heart disease with left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) leads to irreversible diffuse interstitial fibrosis of the myocardium. Sacubitril/valsartan resulted in a reduction in diffuse interstitial fibrosis in following 52 weeks of treatment compared to valsartan alone. Sacubitril/valsartan should be considered in patients with hypertensive LVH, especially those who fail to achieve adequate reduction in diffuse interstitial fibrosis with ACEIs or ARBs. Link to the full text https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-62203-0#Sec8
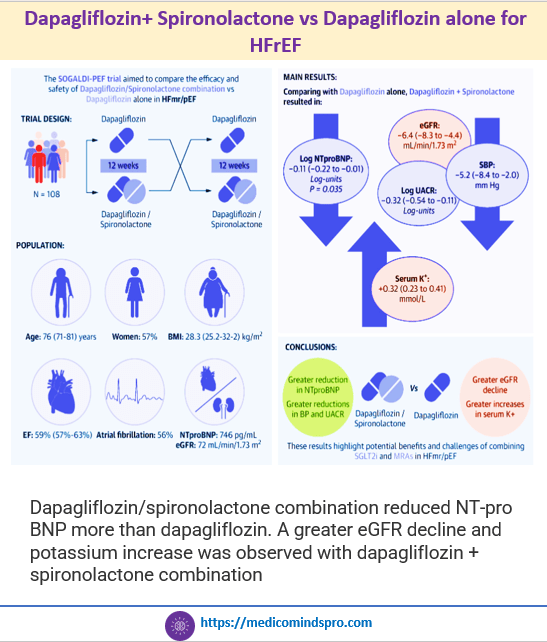
6 Aug 2025: Dapagliflozin+ Spironolactone vs Dapagliflozin alone for HFrEF
Dapagliflozin+ Spironolactone vs Dapagliflozin alone for HFrEF
Dapagliflozin/spironolactone combination reduced NT-pro BNP more than dapagliflozin. A greater eGFR decline and potassium increase was observed with dapagliflozin + spironolactone combination. Link to the full text https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacc.2025.05.033
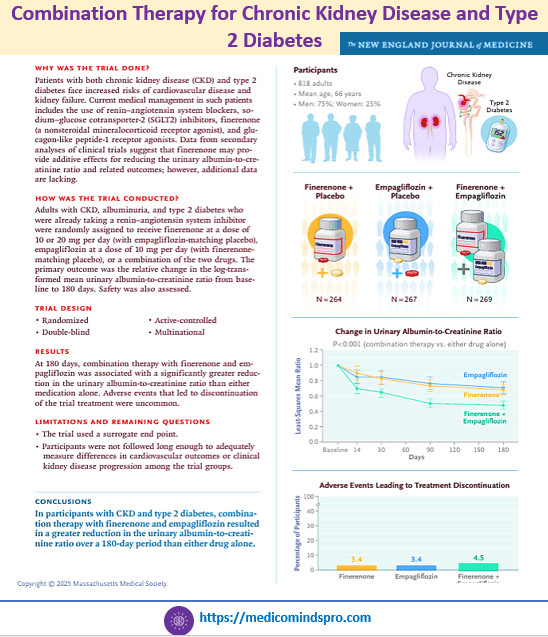
3 Aug 2025: Combination Therapy for Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes
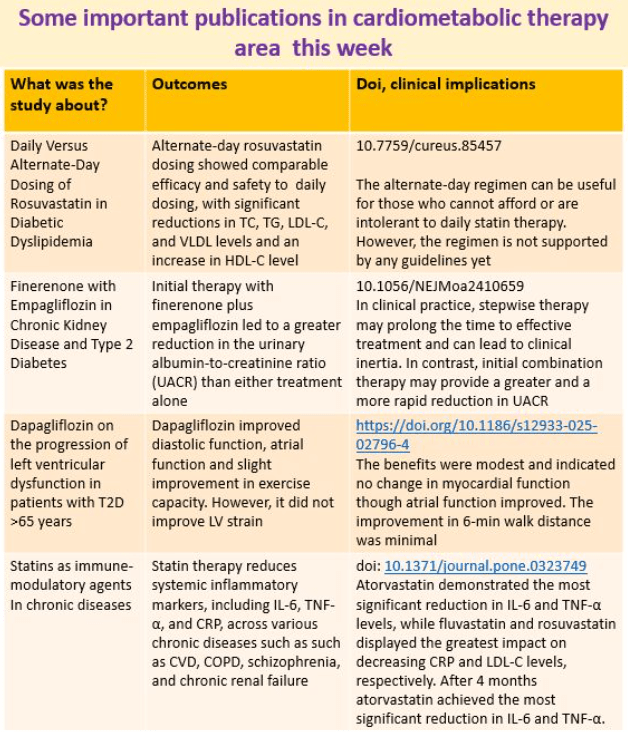
Although previous post hoc and observational analyses of a sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor combined with a nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist in such patients have suggested additive renal benefits, rigorous evidence from randomized trials was lacking. Enrollment of participants with a broad range of urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratios enhances the generalizability of the findings of this study. Link to the full text https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2410659
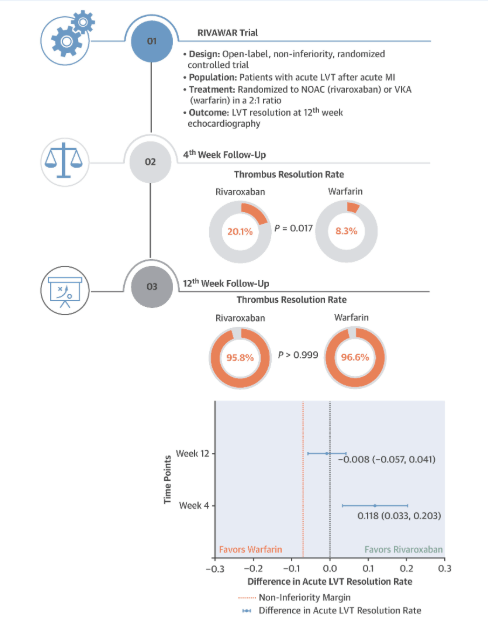
30 July 2025: Rivaroxaban vs Warfarin in Acute Left Ventricular Thrombus Following Myocardial Infarction
This is an important study from a clinician’s perspective because acute left ventricular thrombus is a serious complication of myocardial infarction, with a significant risk of embolic events and death. Warfarin is the standard therapy but has several limitations, like the need for INR monitoring, delayed onset of action, and susceptibility to drug and food interactions
Clinical implications of the findings of this study:
1️⃣ Rivaroxaban is an effective alternative to warfarin for treating acute LVT in post-MI patients.
2️⃣ Rivaroxaban may be particularly advantageous in the acute phase, due to its rapid and predictable anticoagulant effects, leading to timely thrombus resolution
3️⃣ More convenience with rivaroxaban as it does not require strict INR monitoring, unlike warfarin
Here is the full text https://www.jacc.org/doi/10.1016/j.jacadv.2025.101978
25 July 2025: Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on functional outcomes in heart failure patients according to the etiology
Patients with a recent diagnosis of HFrEF and stable clinical status, referred to a heart failure unit, were prospectively enrolled. Exercise capacity was evaluated using the six-minute walk test (6MWT), and quality of life with the Minnesota Living with Heart Failure Questionnaire (MLHFQ) both at baseline and after 6 months. Patients were stratified by etiology and analyzed according to SGLT2i use. SGLT2i improved exercise capacity only in non-ischemic HFrEF patients, suggesting a differential response based on etiology.

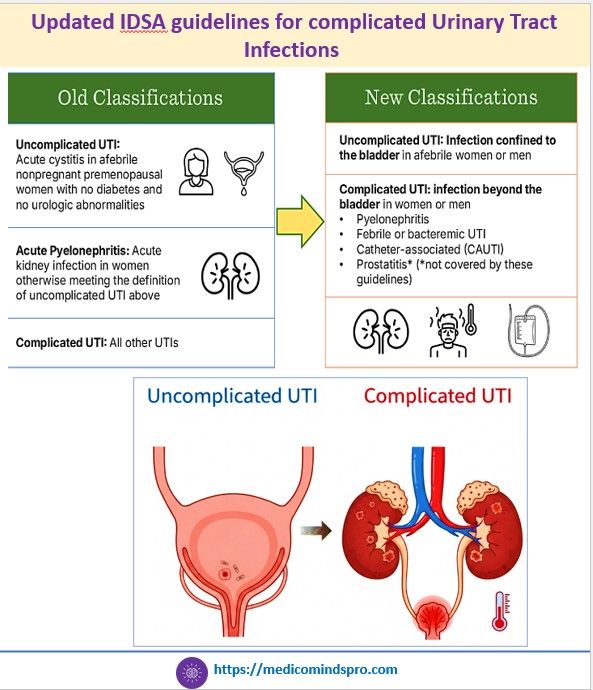
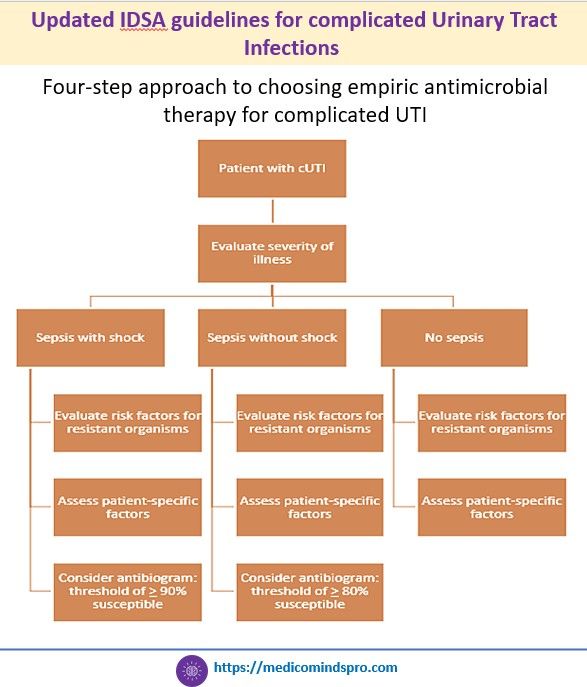
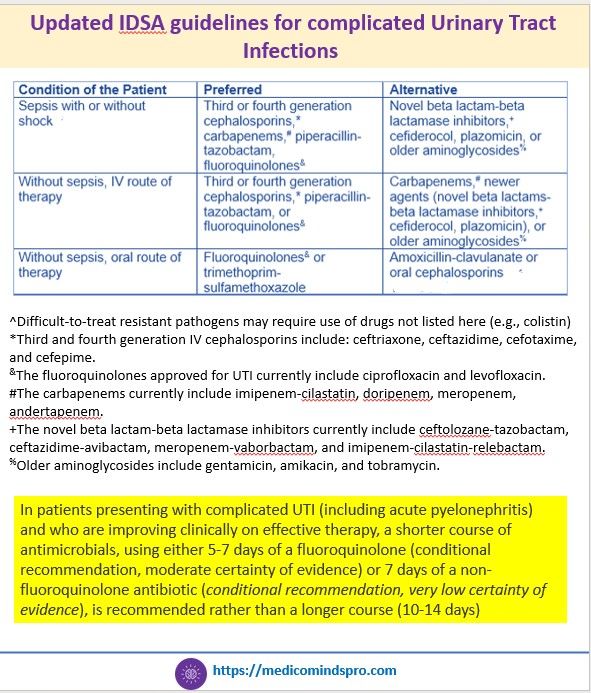
21 July 2025: New IDSA guidelines for complicated Urinary Tract Infections
IDSA has released the first IDSA guidelines on management and treatment of complicated urinary tract infections. The key highlights are shown in the graphics below. The complete guidelines can be found here.
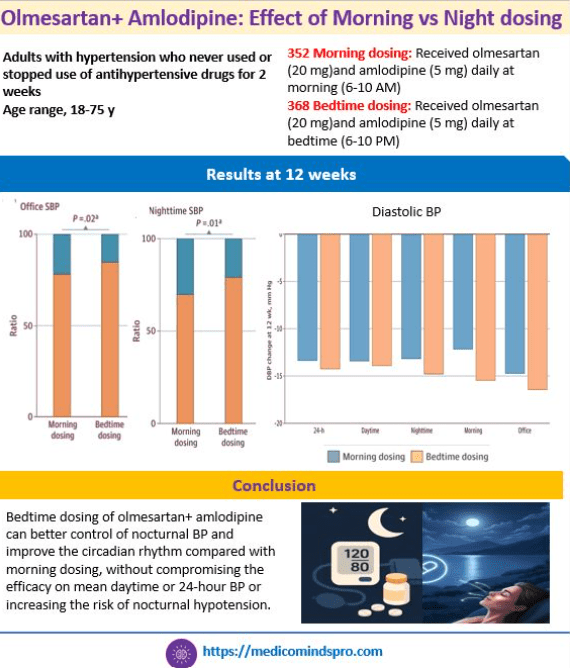
17 July 2025: Olmesartan+ Amlodipine: Effect of Morning vs Night dosing on blood pressure
This new study shows that bedtime dosing of olmesartan+ amlodipine can better control of nocturnal BP and improve the circadian rhythm compared with morning dosing, without compromising the efficacy on mean daytime or 24-hour BP or increasing the risk of nocturnal hypotension.
The paper discusses the importance of nighttime control of BP, as also mentioned in the AHA and ESC guidelines. Further, it also explains why this combination is more effective when taken at night.
Here is the full text of the study https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2836172?utm_campaign=articlePDF&utm_medium=articlePDFlink&utm_source=articlePDF&utm_content=jamanetworkopen.2025.19354
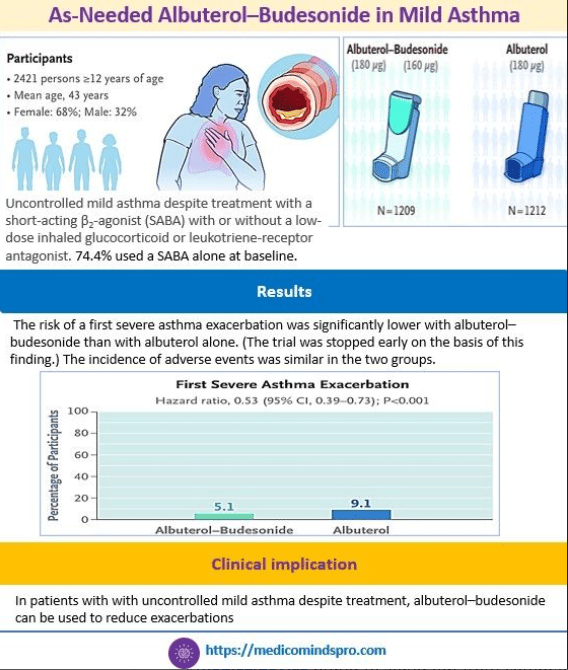
12 July 2025: As-Needed Albuterol–Budesonide in Mild Asthma to prevent exacerbations
A recently published study showed that as-needed use of a fixed-dose combination of albuterol–budesonide resulted in a lower risk of a severe asthma exacerbation than as-needed use of albuterol alone in patients with uncontrolled mild asthma despite treatment.
The link to the new study is here https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa2504544?query=TOC
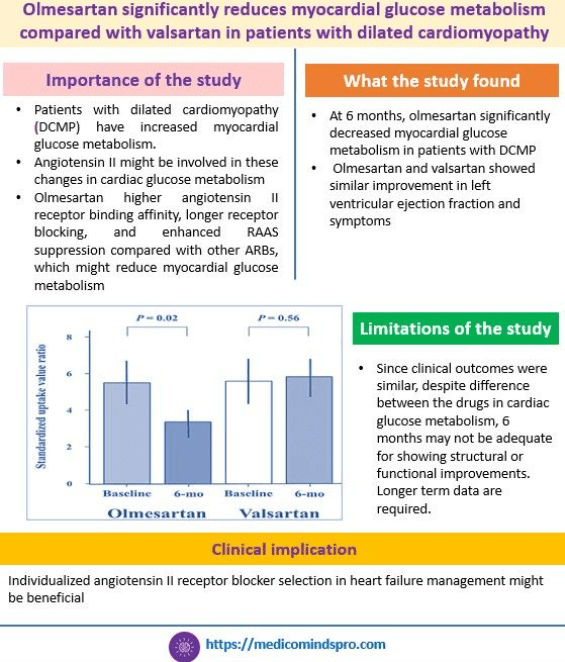
8 July 2025: Olmesartan vs Valsartan in dilated cardiomyopathy
In this new study, 6 months of olmesartan significantly decreased myocardial glucose metabolism compared with valsartan for 6 months, in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. See the graphic below to understand its importance.
The link to the full text of the study is here https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1161/JAHA.125.041406
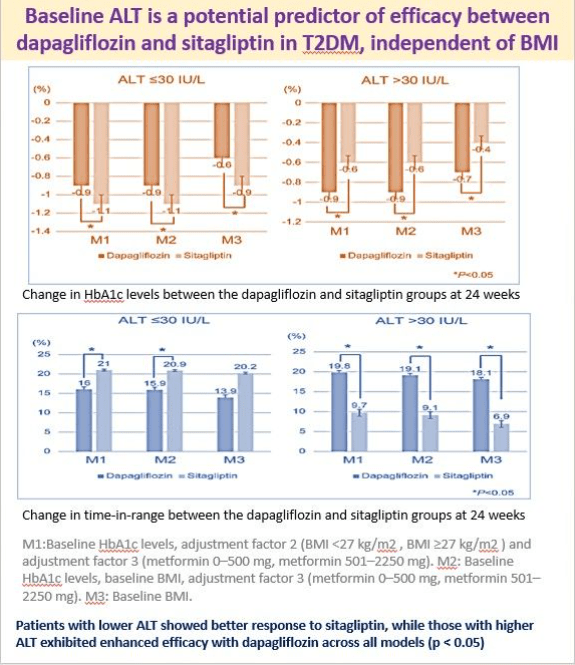
5 July 2025: Baseline ALT is a potential predictor of efficacy between dapagliflozin and sitagliptin
This new publication is a post hoc analysis of the Dapagliflozin Versus Sitagliptin for Type 2 Diabetes–Cardiovascular Risk (DIVERSITY-CVR) study in 340 patients.
Patients with lower ALT at baseline showed a better response to sitagliptin, while those with higher ALT showed enhanced efficacy with dapagliflozin, independent of BMI.
Here is the full text https://dom-pubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/dom.16559?af=R
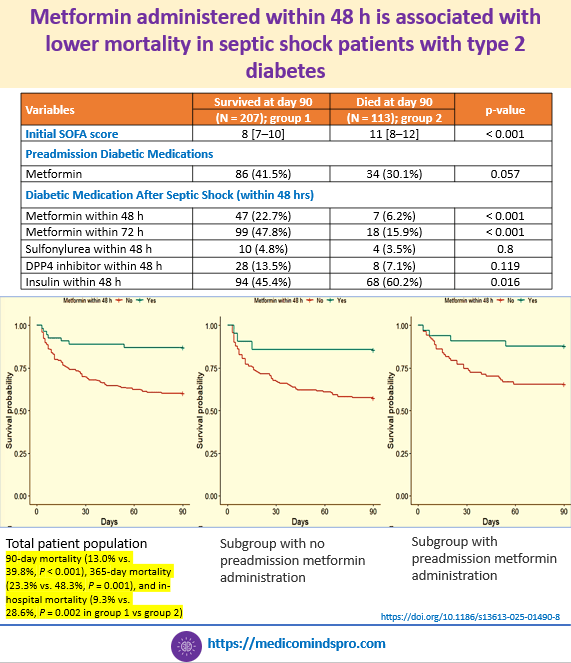
30 June 2025: Metformin administered within 48 h is associated with lower mortality in septic shock patients with type 2 diabetes
This was irrespective of whether patients were taking metformin before the shock.
Do read the full text to understand the inclusion and exclusion criteria and what makes this study unique from previous ones.
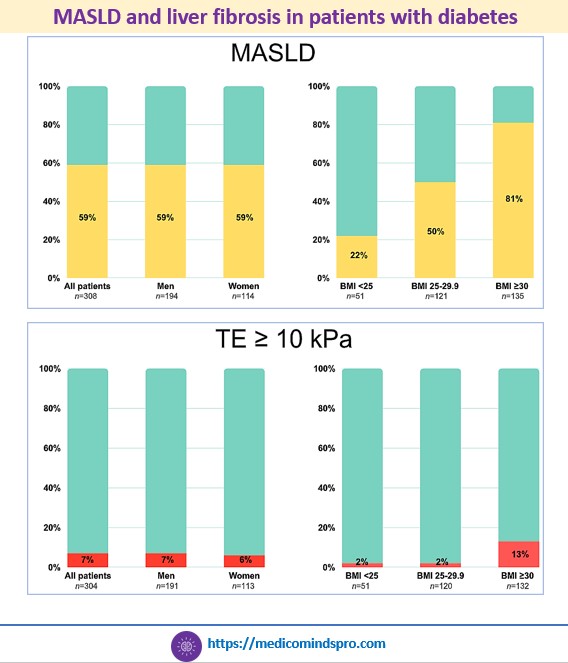
27 June 2025: Which patients with diabetes should be screened for MASLD and liver fibrosis?
Unlike most previous studies conducted in tertiary care centers, this study was conducted among patients visiting primary care and had uncomplicated T2DM.
Patients underwent transient elastography and whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to assess liver fat, cardiac function, muscle composition, and distribution of body fat.
Based on the results, it appears that patients having T2DM and obesity need to be screened as they are at the highest risk.
25 June 2025: clinically relevant publications in Oncology publications of the week
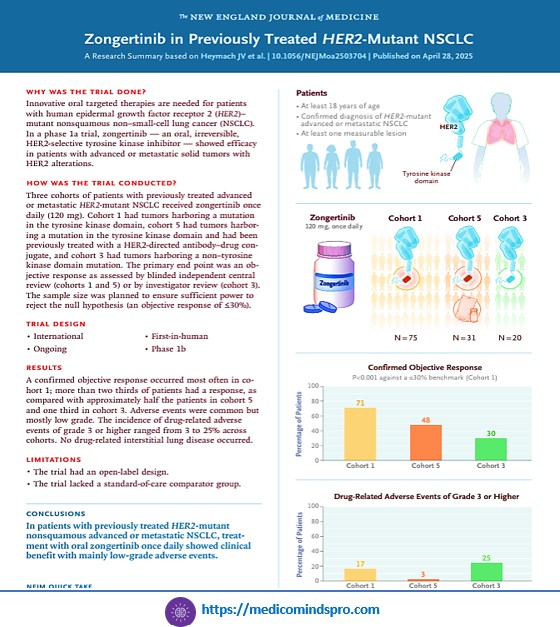
1️⃣ Pembrolizumab extends its strides and enters into the neoadjuvant and adjuvant therapy space in locally advanced head and neck cancer
2️⃣ The first-in-human trial of oral Zongertinib in previously treated patients with HER2-mutant non-squamous NSCLC
3️⃣ Cyclophosphamide and a calcineurin inhibitor showing longer GVHD-free, relapse-free survival than standard prophylaxis (cyclosporin–methotrexate) in patients undergoing allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell transplantation
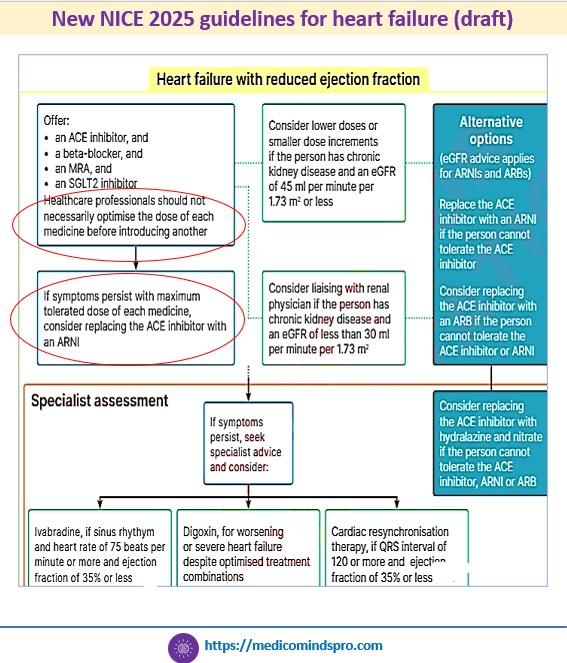
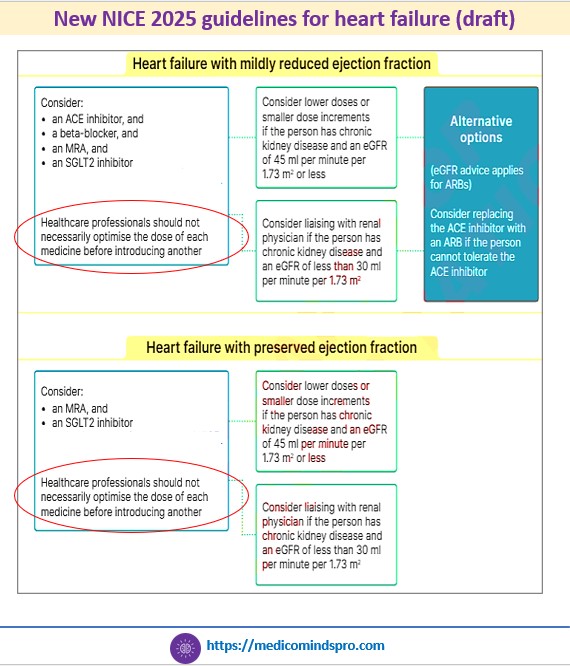
18 June 2025: What has changed in the new NICE guidelines on heart failure?
1️⃣ The four pillars of treatment for HFrEF (Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEI), Beta-blockers, Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists, and
SGLT2 inhibitors) should be prescribed earlier, without the need to optimise the dose of any one medicine before introducing another
2️⃣ SGLT2 inhibitors, such as empagliflozin and dapagliflozin should be offered at the start of the treatment, rather than after other medications have been fully titrated. These are recommended across all types of HF
3️⃣ ARNIs should be prescribed if a person cannot tolerate an ACEI, rather than only to patients who are already taking a stable dose of an ACEI or ARB.
4️⃣ An N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide level < 400 ng/L (47 pmol/L) in an untreated person makes a diagnosis of heart failure less likely.
This is a new draft guidance and is currently open for suggestions from HCPs
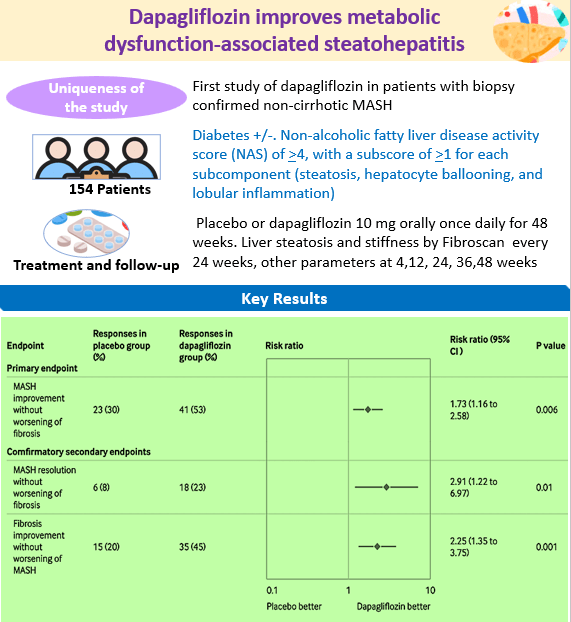
14 June 2025: Improvement in biopsy-proven MASH with dapagliflozin
The endpoints of the study are consistent with the endpoints that the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) proposed as reasonably likely to predict long-term clinical benefit for MASH. Moreover, the improvement was seen in patients with/without obesity and with/without diabetes. Considering that therapeutic options for MASH are limited and pioglitazone has been recommended by the ADA and RSSDI guidelines, this study marks an interesting development.
10 June 2025: Important publications of the week in the cardiometabolic space
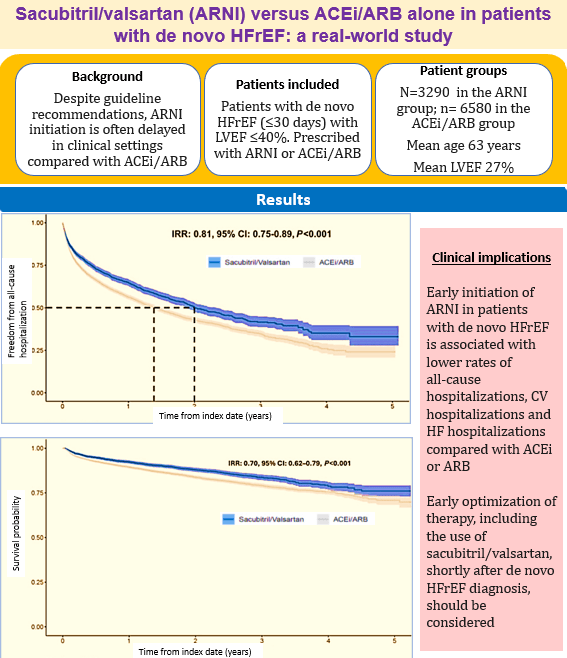
3 June 2025: Sacubitril/valsartan (ARNI) versus ACEi/ARB alone in patients with de novo HFrEF: a real-world study
Real-world study shows that early initiation of ARNI after diagnosis of heart failure with reduced ejection fraction HFrEF is associated with fewer hospitalizations. Read the full text here https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12055388/
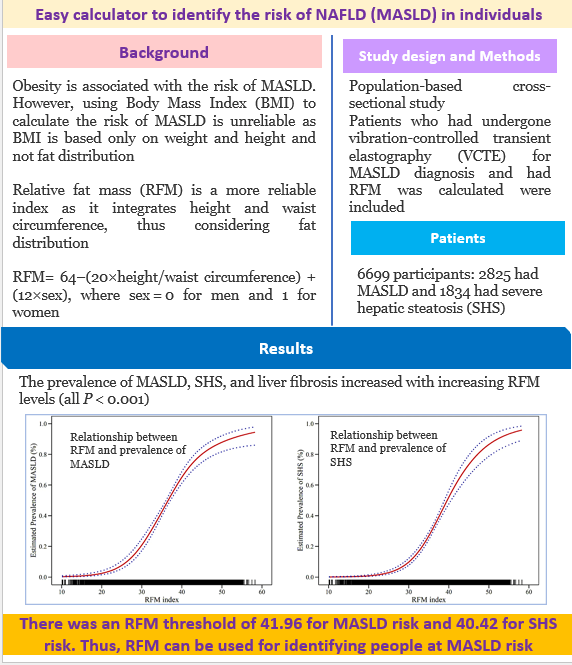
1 June 2025: Easy calculator to identify the risk of NAFLD (MASLD) in individuals
This publication provides an easy calculation for identifying individuals at risk of MASLD and liver fibrosis with clear cut-offs mentioned for the risk. It might be a very useful and handy method for clinicians to identify patients at risk and send them for further investigations. Considering that the incidence of MASLD (NAFLD) is rising and the disease remains asymptomatic until the advanced stages, a simple non-invasive screening tool might help in detecting the disease early.
Here is the full text https://bmcgastroenterol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12876-025-04006-7#Sec193